Many of the biblical stories were plagiarized by the Hebrew nomads Sumerian culture and religion. Today, the Judeo-Christians and many Muslims live with those believing they are original stories of the Jewish people .. Nothing is further from the truth.
CIVILIZATION CHRONOLOGICAL SUMMARY SUMER.
FIRST SETTLERS
In Lower Mesopotamia there were human settlements from the Neolithic culture as evidenced Jarmo, (6700 BC - 6500 BC) and Chalcolithic the of culture Hassuna-Samarra (5500 - 5000 BC), El Obeid (5000 - 4000 BC) Uruk (4000 - 3200 BC) and Nasr Yemdet (3200 - 3000 BC).
Since there are no written records of that period to know the origin of this people, nor found skulls clarify the problem of the origin these people, because they are represented both as dolichocephaly brachycephaly, with some evidence of the type Armeniod. Sumerian sculptures are investigated showing a high rate of brachycephalic skulls in their representations that could perhaps clarify the origin of this village, along with the colors and dimensions of the sculptures, which are a mix of Caucasian and black members. However, this is not enough evidence to solve the problem because the plastic could have been idealized, as happened in the Egyptian sculptures.

The possibility of identifying based on cranial rate developments throughout the Middle East has been ruled out to be quite mixed, however, we can distinguish four groups with the main features of each from different periods: before 4000 a. C., dolichocephalic populations are only such as "Mediterranean", the "eurafricanos", which is only one variety of it that did not have a significant role to 3,000 a. C.; type "alpine" manifest moderately brachycephalic after 2,500 a. C., and "Armeniods", derived perhaps from these Alpine appear in abundance after in 500 BC C. The peoples descended from the Cimmerians on average tend to have more heads "rounded" (brachycephalic) than the other peoples of that area and the word "Sumerian" may be a transliteration of the word "Cimmerian" according to some philologists , which is why many researchers believe that both peoples are the same people at different times, but there is insufficient evidence to support this hypothesis.
seems possible that the Sumerians were a tribe from outside, possibly from the steppes, but its specific origin is unknown. This is what has come to be known from the twentieth century as the "Sumerian problem."
However, during the period of progress occurs Obeid crystallizing Uruk to consider it as the beginning of the Sumerian civilization.
URUK PERIOD
Uruk, the biblical Erech and Arabic Warka, is the scene of fundamental discoveries in the history of mankind: the wheel appears by the 3500 a. C. and writing in the 3300 a. C., which is the oldest dating of clay tablets with cuneiform found to date. Are these written records which confirm that the Sumerians were not Indo-European people, nor a bed nor ELAM-Semitic nor Dravidian (group, the latter, to which the Elamite people, for example). This is evidenced by his tongue-type binder. Thus it is speculated, as has been said that the Sumerians were not the first people to settle in Mesopotamia, in the lower reaches of the Fertile Crescent, but came at a certain time of the Copper Age or Chalcolithic , beyond the year 3500 BC, during the period now known as U. Dynastic Period
ARCHAIC
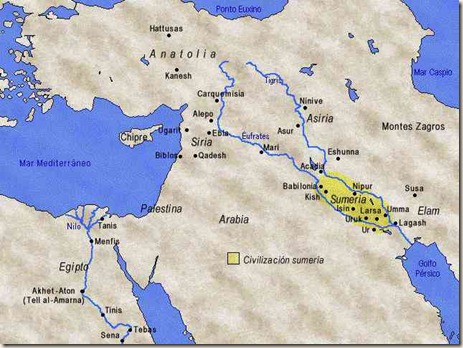
 Situation of the main Sumerian cities and scope of this culture during the archaic dynastic period.
Situation of the main Sumerian cities and scope of this culture during the archaic dynastic period.
The dissemination of the progress of the Uruk culture for the rest of Mesopotamia gave birth to the Sumerian culture. These techniques allowed the growth of cities across new territories. These cities will soon be characterized by the appearance of walls, suggesting that the wars between them were frequent. It also highlights the expansion of writing that sprang from its administrative and technical role to the first dedicatory inscriptions in enshrined statues of the temples.
Despite the existence of the Sumerian king lists the history of this period is relatively unknown as much of the reigns have dates set out in them impossible. In fact, these lists were made from the seventeenth century a. C., and its creation was probably the desire of monarchs traced their lineage back to epic times. Some of the kings are probably real, but in many others there is no historical record and others who know their existence is not contained therein.
DOMAIN ARCADIO
A. 2350 C., Sargon, an Akkadian source usurper, seized power in the city of Kish . He founded a new capital, Agade and conquered the other Sumerian cities, beating Lugalzagesi , the king of Umma hitherto dominant. This was the first great empire in history and would be continued by the successor of Sargon, which would have to face constant riots. Among them, the grandson of the conqueror, Naram-Sin . This step marked the beginning of the decline of the Sumerian language and culture for the Acadians.
The empire broke into 2220 a. C., due to constant riots and the invasions of the nomadic Amorites and mainly Gutians . After his fall, the entire region fell under the domination of these tribes, who were imposed on the city-states of the region, especially in the vicinity of the destroyed Agade. Sumerian chronicles describe consistently negative, as "barbarian hordes" or "dragon mountain", but reality may not be so negative, in some schools there was a real flowering of the arts. This is the case in the city of Lagash , especially during the rule of Gudea patesi . Addition artistic quality in works of Lagash were used materials from remote regions: Lebanese cedar wood or greenstone, gold and carnelian from the Indus Valley, suggesting that trade should not see especially burdened. Southern cities, furthest from the center of power guti, bought his freedom in return for large taxes; Uruk and Ur prospered during his fourth and second dynasties.
SUMERIAN RENAISSANCE Renaissance
According to a memorial tablet was hengal Utu-king of Uruk, who in about 2100 a. C. defeated and expelled Gutians the rulers of the Sumerian lands. Its success will not be of much benefit since shortly after the king of Ur, Ur-Nammu , achieved hegemony in the region with the so-called Third Dynasty of Ur or Sumerian Renaissance. The rule emerged from this hegemony would be as long or more than that of Sargon, which would take the idea of \u200b\u200bunifying the empire. This influence is evident even in the name of the monarch, who in imitation of the Acadians will be called "kings of Sumer and Akkad"
A Ur-Nammu will happen to his son, Shulgi , who fought against Elam and nomadic tribes of the Zagros . He was succeeded his son Amar-Suen it first and his brother, Shu-Sin and then another Ibbi-Sin. In the latter's reign the attacks of the Amorites, from Saudi, became particularly strong in 2003 a. C. last fall predominantly Sumerian empire. Henceforth it will be the Akkadian culture which predominates and then Babylon inherit the role of Sumerian empires.
UR III PERIOD
The disappearance of the Akkadian Empire allowed Sumer renaissance and return to the city-states regime. Are highly relevant reforms II Gudea of \u200b\u200bLagash dynasty in this Neo-Sumerian period (2175 BC). Later in the Third Dynasty Deur, Ur-Nammu conducts a well structured code with numerous changes. In this age are beginning to appoint as Kings of Sumer and Akkad (2111 BC). Shulgi in 2093 a. C. promote developments relating to weights and measures, to strengthen the border while the harassment of Semitic - Amorites.
Nevertheless, he finally succumbed to the attacks of the Amorites (Amorites) who auxiliaries had -Semitic Elamites, from the plateau of Iran, who prevailed and plundered Ur (2003 BC). It becomes a state of political fragmentation and proliferating local dynasties. Rimsin created a small empire in 1792 a. C. where private property was introduced, giving a pre-capitalist society. In contrast, in Babylon is enthroned an Amorite dynasty (1792 BC).
Society of the Third Dynasty of Ur is organized as follows:
- mashda "seconds." Eren
- "crowd of the palace." Maybe it is bonded or court of the palace.
- go / game: bred (free). Parents sold their children to the temple but the children do not lose their freedom for this condition.
- Nimr: slaves. They are distinguished by wearing a collar with the name or a tuft of hair on the head.
RELIGION AND BELIEF
Literature Sumerian LiteratureOde to iddin-Dagan, king of Larsa . Registration Sumerian cuneiform in , around 1950 a. C.
Sumerian literature covers three broad topics: myths, hymns and lamentations. The myths are composed of short stories that try to shape the personality of the Mesopotamian gods: Enlil, chief god and father of the minor deities; Inanna, goddess of love and war, or Enki, god of water frequently faced Ninhursag , goddess of the mountains. The hymns are texts in praise of gods, kings, cities and temples. The issues relate lamentations catastrophic destruction of cities and temples and the abandonment of resulting gods.
Some of these stories may rely on historical events such as wars, floods or construction activity for a king importantly, magnified and distorted over time.
own creation Sumerian literature was a kind of poetry dialogues based on the opposition of contrary concepts. Proverbs also an important part of the Sumerian texts.
Like the people who have not been civilized, the Sumerians were the movements around him as the spirit magic, magic that was the only explanation I had of how things worked. These spirits were their gods. And with many spirits around, they believed in many gods, they had human emotions. Believed that the sun, moon and stars were gods, like the reeds that grew around the beer and distilled.
believed that the gods controlled the past and the future, that God revealed to them that they possessed skills, including writing, and the gods gave them everything they needed to know. They had the view that their civilization had been developed by their own efforts. And they had no vision of technological or social progress.
Each of the Sumerian gods (in their own language, dingir and pluralism, Ding-Ding or dingira-ne-ne ) was associated with different cities, and religious importance attributed to them intensified or declined depending on the political power of the associated city. According to Sumerian tradition, the gods created humans from clay in order to be served by their new creation. When they were angry or frustrated, the Gods expressed their feelings through earthquakes and natural disasters: the primordial essence of Sumerian religion was based, therefore, in the belief that all humanity was at the mercy of the gods.

Major mythological figures worshiped by the Sumerians, it is possible to cite: An
- (or Anu), god of heaven
- Nammu , the mother goddess;
- Inanna, the goddess of love and war (equivalent to the goddess Ishtar of the Akkadian);
- Enki eRide the temple, the god of beneficence, driver of freshwater from deep under the earth;
- Utu in Sippar , the sun god;
- Nanna, the moon god in Ur;
- and Enlil, the god of wind.
The Sumerians were probably dug in the ground a few feet and found water. The Sumerians believed that the earth was a great album floating in the sea. They called this sea Nammu and thought it had always been in time. Nammu believed had created the fish, birds, wild pigs and other creatures that appeared in the marshes and wetlands.
According to them, Nammu had created heaven and earth. The sky was separated from the earth , giving birth to the male god An and the earth, a goddess called Ki. An believed that Ki and had fathered a son called Enlil, who was the atmosphere, wind and storm. They believed separated day from night and had opened an invisible shell water dropping from the sky. believed that along with his mother and Ki, Enlil laid the foundation for the creation of plants, humans and other creatures that did germinate the seeds and had shaped mankind from clay, impregnating.
The universe consisted of a flat disk enclosed by a dome of brass. Life after death involved a vile descent into the underworld, where he spent eternity in a deplorable existence, a kind of hell.
believed that growing crops because a male god was mating with his goddess wife. They saw hot, humid months of summer, when the fields and meadows were stained brown, as the moment of death of the gods. When fields bloomed again in the fall, they believed that their gods resurrected. Mark this as the beginning of the year, which was held in their churches with music and songs.
did not believe in social change, although Sumerian priests had altered the stories, creating new twists on old tales; not recognize this as a change induced by humans or wondering why they had failed to do it right the first time. The new ideas were simply revelations of their gods.
were different types of priests. Some of the most common were:
- āšipu , exorcist and medical.
- baru, astrologer and soothsayer.
- qadištu , priestess.
Sumerian temples consisted of a nave with runners on both sides, flanked by rooms for the priests. At one end of the corridor was a pulpit and a platform built of mud bricks, used to sacrifice animals and plants.
barns and warehouses are generally located in the vicinity of temples. Later, the Sumerians began to build their temples on top of artificial hills, terraced and multifaceted: these special temples called ziggurats .


0 comments:
Post a Comment